Friday 9 March 2012
Tuned Mass Damper
Research Assignment
In order to prevent buildings and other structures from continuing to vibrate at their natural frequencies, engineers add tuned mass dampers to the structure.
1. What is a tuned mass damper?
2. What sort of structures need a TMD?
3. Provide an example of one structure with a TMD and what the TMD's parts are made of.
4. How does a TMD work?
Provide all links you used in finding your information. Your answers should be HAND WRITTEN.
Thursday 2 February 2012
Physics in the News Assignment
This assignment is due Wednesday, February 8.
Physics is around in the news all the time.
Just last January Saskatchewan decided to invest money in researching how to create medical isotopes without using a nuclear reactor.
Your assignment is to find a news article relating to some aspect of Physics from the past year.
This assignment will be marked on the following criteria:
Total /10
Physics is around in the news all the time.
Just last January Saskatchewan decided to invest money in researching how to create medical isotopes without using a nuclear reactor.
Your assignment is to find a news article relating to some aspect of Physics from the past year.
- Print out or cut out the article
- Write a summary or explanation of the article in your own words
- Compile your article and your written portion into a display/poster that can hang on the wall
This assignment will be marked on the following criteria:
- The article is recent and relevant /2
- * Provide the link/reference
- The summary is in your own words /2
- The summary clearly explains the content of the article /4
- The display is visually appealing /2
Total /10
Friday 6 January 2012
Subtractive Theory of Color
Opaque Objects:
When white light shines on an opaque object such as a red apple all the colors except red will be absorbed into the object except red. The color red will hit the object and reflect off of it to appear red.
Transparent Objects:
When white light hits a transparent object like a blue waterbottle all the colors except for blue will be absorbed. the blue color will reflect as well as travel through the object.
Compound Filters:

This shows when white light hits a yellow compound filter the colors yellow, orange and green will be transmitted through while the rest are absorbed. Then they continue to hit a blue compound filter which only allows the green color to pass through, so your results are the color green.]
*If an object is black that means all the colors from the white light are being absorbed into the object.
*If an object is white this means that no colors are being absorbed they are all being reflected off the object.
We also looked at adding colors together to see what it would produce.

Whoever is left can write the blog.
Opaque Objects:
When white light shines on an opaque object such as a red apple all the colors except red will be absorbed into the object except red. The color red will hit the object and reflect off of it to appear red.
Transparent Objects:
When white light hits a transparent object like a blue waterbottle all the colors except for blue will be absorbed. the blue color will reflect as well as travel through the object.
Compound Filters:

This shows when white light hits a yellow compound filter the colors yellow, orange and green will be transmitted through while the rest are absorbed. Then they continue to hit a blue compound filter which only allows the green color to pass through, so your results are the color green.]
*If an object is black that means all the colors from the white light are being absorbed into the object.
*If an object is white this means that no colors are being absorbed they are all being reflected off the object.
We also looked at adding colors together to see what it would produce.

Whoever is left can write the blog.
Polarization
today in class we learned about polarization
polarization involves the use of a polaroid filter. Polaroid filters are made of a special material that is capable of blocking different amounts of light.
When light is transmitted through a Polaroid filter, it emerges with one-half the intensity it emerges as polarized light.
Polarization of light by use of a Polaroid filter are used to look through and view objects. The filter does not distort the shape or dimensions of the object; it merely serves to produce a dimmer image of the object since one-half of the light is blocked as it passed through the filter. A pair of filters is often placed back to back in order to view objects looking through two filters. By slowly rotating the second filter, an orientation can be found in which all the light from an object is blocked and the object can no longer be seen when viewed through two filters.
the light was polarized upon passage through the first filter blocked by the second filter since its polarization filter is aligned in a horizontal direction.
While you are unable to see the axes on the filter, you will know when the axes are aligned perpendicular to each other because with this orientation, all light is blocked. So by use of two filters, one can completely block all of the light that is incident upon the set; this will only occur if the polarization axes are rotated such that they are perpendicular to each other.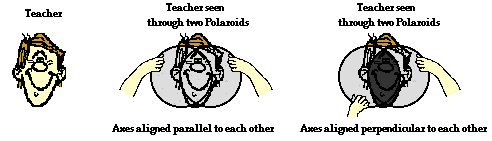
we ended the class by working on our unit reviews.
polarization involves the use of a polaroid filter. Polaroid filters are made of a special material that is capable of blocking different amounts of light.
When light is transmitted through a Polaroid filter, it emerges with one-half the intensity it emerges as polarized light.

Polarization of light by use of a Polaroid filter are used to look through and view objects. The filter does not distort the shape or dimensions of the object; it merely serves to produce a dimmer image of the object since one-half of the light is blocked as it passed through the filter. A pair of filters is often placed back to back in order to view objects looking through two filters. By slowly rotating the second filter, an orientation can be found in which all the light from an object is blocked and the object can no longer be seen when viewed through two filters.
the light was polarized upon passage through the first filter blocked by the second filter since its polarization filter is aligned in a horizontal direction.
While you are unable to see the axes on the filter, you will know when the axes are aligned perpendicular to each other because with this orientation, all light is blocked. So by use of two filters, one can completely block all of the light that is incident upon the set; this will only occur if the polarization axes are rotated such that they are perpendicular to each other.

we ended the class by working on our unit reviews.
Tuesday 20 December 2011
Optics
We began class by reviewing applications of optics:
Stereoscopic Vision
We are able to perceive our depth perception by the use of binocular vision. An object must be imaged by two cameras to view a 3D image as each of our eyes receives a different image, This can be done by the use of anaglyphs, color filter glasses and a head mount display.
Microscope
Microscopes use converging lenses to magnify objects too small for the eye to see. To obtain larger images two or more lenses are combined to make a simple compound microscope.
Projector
Two converging lenses in a projector refract light so that an object is uniformly illuminated. The object is placed a distance of one of two focal lengths in front of the projection lens, resulting in a large real image.
Camera
Light enters a camera lens system and strikes a plane mirror. Light is reflected up to the pentaprism where total internal reflection guides the light through the viewfinder. When the photograph is snapped the mirror lifts up and allows light to strike the film.
We then wrote our quizzes on ray diagrams and thin lens equations as well as discuss various eye prescriptions. If you have 20/20 vision, it means that when you stand 20 feet away from an object you see what the 'normal' person sees at 20 feet. Examples of prescriptions are -3.5, 7.1.
Stereoscopic Vision
We are able to perceive our depth perception by the use of binocular vision. An object must be imaged by two cameras to view a 3D image as each of our eyes receives a different image, This can be done by the use of anaglyphs, color filter glasses and a head mount display.
Microscope
Microscopes use converging lenses to magnify objects too small for the eye to see. To obtain larger images two or more lenses are combined to make a simple compound microscope.
Projector
Two converging lenses in a projector refract light so that an object is uniformly illuminated. The object is placed a distance of one of two focal lengths in front of the projection lens, resulting in a large real image.
Camera
Light enters a camera lens system and strikes a plane mirror. Light is reflected up to the pentaprism where total internal reflection guides the light through the viewfinder. When the photograph is snapped the mirror lifts up and allows light to strike the film.
We then wrote our quizzes on ray diagrams and thin lens equations as well as discuss various eye prescriptions. If you have 20/20 vision, it means that when you stand 20 feet away from an object you see what the 'normal' person sees at 20 feet. Examples of prescriptions are -3.5, 7.1.
Notes:
Opticians prefer to use the optical power P of a lens instead of a focal length. Power is measured in diopters (D).
P= 1/f
f must be in meters to have P to be in Diopters.
The optical power is positive for converging lens and negative for diverging lenses. The higher the optical power the shorter the focal length.
Example
1. A nearsighted person can focus on objects no father than 20.0 cm from the eye. What power of a lens is needed to enable the eye to focus the eye on distant objects clearly?
First identify whether they need a converging or diverging lens.
Diverging. Object is distant.
do= infinity
f= ?
di= -20.0com
1/di+ 1/do = 1/f
1/-20 + 1/infinity =i/f
= 0
The next person to go must be the quickest at saying the alphabet backwards. :)
Monday 19 December 2011
Telescopes
We were given class time to finish the Thin-Lens Practise Problems. Here are the answers:
Telescopes
To view distant objects such the moon and stars with detail, two or more lenses must be used together. The images are smaller but since they are much closer they appear larger.
Galilean Telescope

This telecope uses both converging and diverging lenses. The image produced is virtual, upright and larger.
Reflecting Telescope
Refracting Telescope

This telescope uses two converging lenses. The image produced is virtual, inverted and larger.
Terrestrial Telescope
 This telescope uses three converging lenses, the third lens located in the middle (erector lens) has the purpose of inverting the image so it is upright like the object. Images produced are virtual, upright and larger.
This telescope uses three converging lenses, the third lens located in the middle (erector lens) has the purpose of inverting the image so it is upright like the object. Images produced are virtual, upright and larger.
The next blog writer will be anybody who has not written and sits by the windows of the classroom
- di= 36cm hi= -3.6cm
- di= -15cm hi= 2.5cm
- a)di= 510cm b)hi= -62.5
- di= -30cm hi= 1.8cm
- di=do= 5.0cm
- di= -14cm f=4.7cm
Telescopes
To view distant objects such the moon and stars with detail, two or more lenses must be used together. The images are smaller but since they are much closer they appear larger.
Galilean Telescope

This telecope uses both converging and diverging lenses. The image produced is virtual, upright and larger.
Reflecting Telescope

Refracting Telescope

This telescope uses two converging lenses. The image produced is virtual, inverted and larger.
Terrestrial Telescope
 This telescope uses three converging lenses, the third lens located in the middle (erector lens) has the purpose of inverting the image so it is upright like the object. Images produced are virtual, upright and larger.
This telescope uses three converging lenses, the third lens located in the middle (erector lens) has the purpose of inverting the image so it is upright like the object. Images produced are virtual, upright and larger. The next blog writer will be anybody who has not written and sits by the windows of the classroom
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

